· Alexander · GitHub · 6 min read
GitHub Actions - Automating your Docker Builds with Diun
Automate your docker builds using Diun

In my previous post, we got our GitHub Actions pipeline set up and built our first Docker container image based on Caddy. In this post, we will be covering the process of automating the pipeline based on upstream changes in the parent Caddy Docker image. For this we will be deploying a service called Diun on a local docker machine.
What is Diun?
**D**ocker **I**mage **U**pdate **N**otifier is a CLI application written in Go and is delivered as a single executable (and as a Docker image) to receive notifications when a Docker image is updated on a Docker registry.
Diun is a cool utility that watches a docker registry for updates and can run notifications based on them.
The Environment
I will be running this series as if you were running on Windows 10/11 with Visual Studio Code installed. Now this series can also be followed fairly easily if you are running Linux setup or WSL. I am also assuming you have a general understanding of the command line interface. If you need more help, leave a comment below and I will reach out!
Pre-Requisites
You should have these items created and set up before following this post.
- Have a Linux machine running Docker
- Have SSH access to the Docker machine
- Have an SSH client installed or have OpenSSH client enabled if running on Windows 10/11.
- Completed the previous post.
Deploying Diun
Before we deploy Diun we need to setup the directory for Diun to house configuration files in. SSH to your Docker machine and run the following commands:
mkdir ~/diunmkdir ~/diun/scriptsmkdir ~/diun/dataNow create the following files:
cd ~/diuntouch docker-compose.ymltouch config.ymltouch /scripts/caddy.shtouch /data/images.ymlYour directory should now look like this tree output:
diun├── scripts│ └── caddy.sh├── data│ └── images.yml├── config.yml└── docker-compose.ymlConfiguring Diun
Now that we have our directory and file structure ready for Diun, we need to tell it what to do. First edit the config.yml file.
nano config.ymlAdd the following info to the file:
#config.ymlwatch: workers: 1 schedule: "0 */6 * * *"providers: file: filename: /data/images.ymlnotif:# Enable this if you would like to post update notifications to a discord channel via a webhook.# discord:# webhookURL: <https://discordwebhookurl.com># timeout: 10s script: cmd: "sh" args: "/scripts/caddy.sh"CTRL + X then Y to save and close the file. Now lets edit the images.yml file.
nano /data/images.ymlAdd the following info to the file:
#images.yml- name: docker.io/caddy:latestCTRL + X then Y to save and close the file. Now edit the caddy.sh script file.
nano /scripts/caddy.shCopy the following info into the file. Make sure to edit the <TOKEN>, and <git_repo> (username/repo) portions.
#!/bin/bash#caddy.sh
curl -H "Accept: application/vnd.github.v3+json" \ -H "Authorization: token <TOKEN>" \ --request POST \ --data '{"event_type": "caddy"}' \ https://api.github.com/repos/<git_repo>/dispatchesCTRL + X then Y to save and close the file. Finally edit the docker-compose.yml file.
nano docker-compose.ymlCopy the following info into the compose file.
#docker-compose.ymlversion: "3"services: diun: restart: always image: crazymax/diun:latest volumes: - "/opt/docker/diun/data:/data" - "/opt/docker/diun/scripts:/scripts:ro" - "/opt/docker/diun/diun.yml:/config.yml:ro" - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock" environment: - "TZ=America/New_York" - "LOG_LEVEL=info" - "LOG_JSON=false"CTRL + X then Y to save and close the file.
Starting Diun
Now that we have all of our config/script files configured we can start Diun. While in the ~/diun directory, run:
docker compose up -dNow that Diun is running, we can test the script to make sure its able to fire off our Actions pipeline. To make sure Diun can access the script and run it, we need to exec into the Diun container.
docker exec -it diun-diun-1 /bin/shOnce inside the container we can navigate to the scripts directory and run the caddy.sh script.
cd /scriptssh caddy.shAfter the script completes you can exit the container environment by typing exit. Next open your GitHub repository and navigate to the Actions tab. You should see a new active entry that was triggered by a repository dispatch. See below picture for an example of a completed action run by a repository dispatch.
 Example of a completed GitHub Actions run triggered by repository dispatch
Example of a completed GitHub Actions run triggered by repository dispatch
With that, all we need to do now is wait until the Caddy base image updates! Here is what the container log looks like when Diun successfully initiates an update notification.
Fri, 06 May 2022 18:00:00 EDT INF Cron triggeredFri, 06 May 2022 18:00:00 EDT INF Found 1 image(s) to analyze provider=fileFri, 06 May 2022 18:00:01 EDT INF Image update found image=docker.io/library/caddy:latest provider=fileFri, 06 May 2022 18:00:02 EDT INF Jobs completed added=0 failed=0 skipped=0 unchanged=0 updated=1Fri, 06 May 2022 18:00:02 EDT INF Next run in 5 hours 59 minutes (2022-05-07 00:00:00 -0400 EDT)The log output shows Diun found an image update for Caddy which fired off our notification setup. In my case it ran the script to update my image, as well as post a notification to my personal discord server:
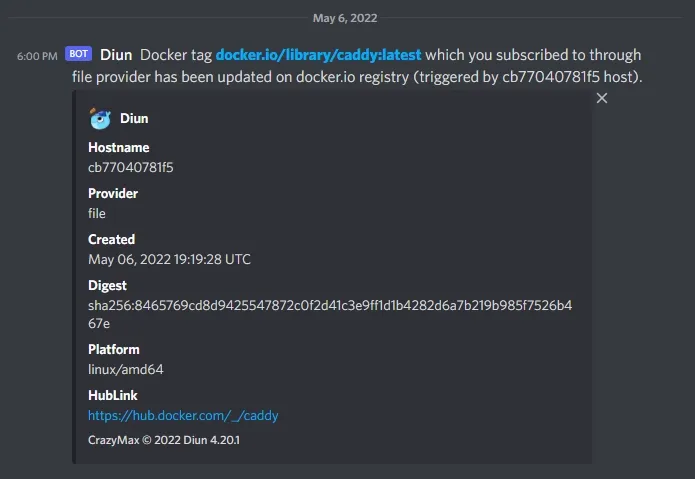 Discord notification from Diun about an image update
Discord notification from Diun about an image update
Let me know down below if you run into any issues and stay tuned for Part 3!
Thanks to my good friend Stefan for helping proof this post series!